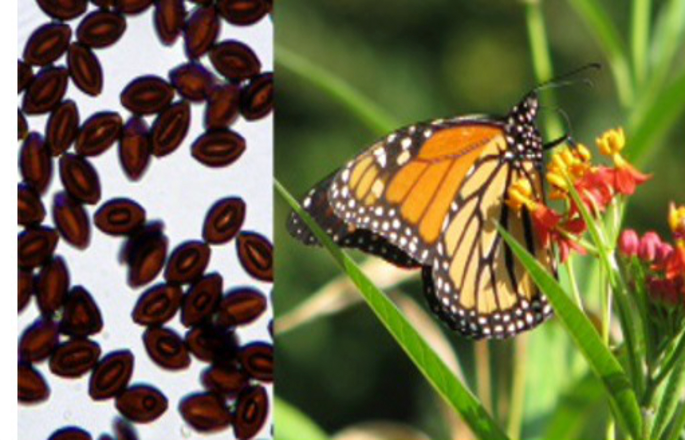
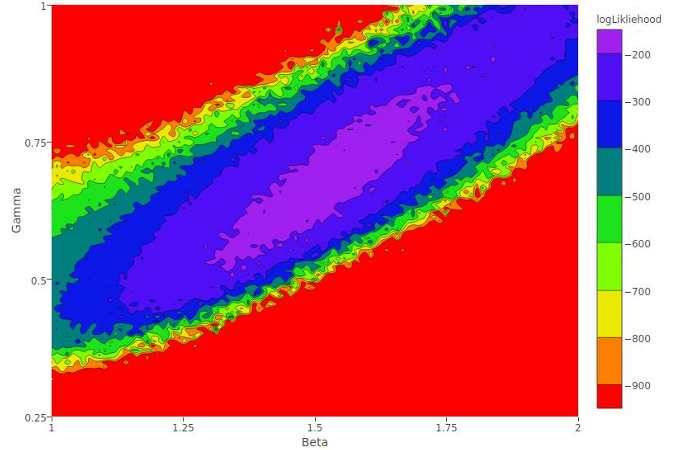
Behavioral and environmental determinants of parasite transmission in a butterfly host
Chastity Ward, a senior from Fayetteville State University, worked on a project with Dr. Sonia Altizer, Dr. Richard Hall and Dr. Paola Barriga to examine how parasites of the Monarch butterfly are transmitted. Abstract: Many pathogens can be transmitted when infectious stages shed into the environment are later encountered by susceptible hosts. Environmental transmission is